We use cookies to make its website more user-friendly, secure and effective. Cookies collect information about the use of websites. Further information: Information on data protection

Mortgage rate trends in Switzerland.
The current most attractive mortgage interest rates.
Saron mortgage from*
Fixed-rate 10 years from
Fixed-rate 5 years from
Mortgage rate trends in Switzerland.
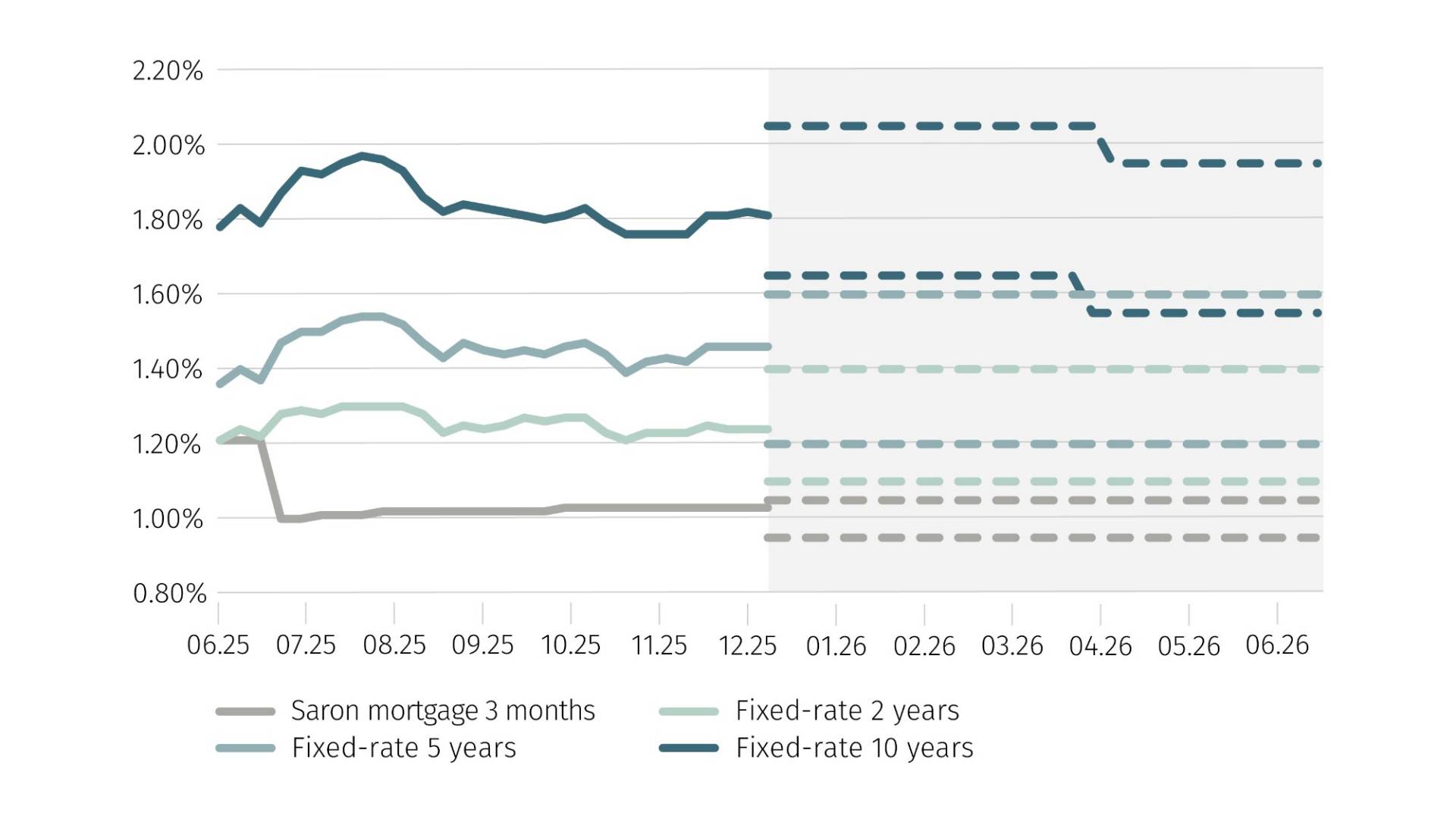
Mortgage interest rates have been largely stable since summer 2025. Inflation remains low in Switzerland, while the Swiss franc has appreciated slightly and the economy, particularly industry and exports, is cooling. SECO is forecasting a slowdown in Swiss economic growth from 1.3% (2025) to 0.9% in 2026. Uncertainty about the long-term trend continues to be reflected in the large interest rate differential between short- and long-term mortgages. Mortgage takers are increasingly opting for medium-length terms of five to nine years.
Mortgage interest rate forecast to mid-2026
If the impact of US tariff policy and geopolitical conflicts stays within the expected range, there is reason to believe that mortgage rates will continue to be attractive. Inflation in Switzerland remains stable at a low level, and the national currency is currently very resilient against the euro and dollar. Accordingly, the base rate is expected to sit at zero for an extended period of time. If this materialises in the first quarter of 2026, interest rates for long-term fixed-rate mortgages are likely to ease slightly by mid-2026, while rates on short- and medium-term mortgages and Saron mortgages appear to have already bottomed out.
Note: Predictions regarding future rate trends are highly complex, so should always be regarded as an estimate as opposed to a precise indicator.